What Are the Rules of Naturalization?
Becoming a U.S. citizen through naturalization is a life-changing process for many immigrants. At Law Offices of Jeffrey A. Thompson, we often receive questions about what the rules of naturalization are.
This blog post will outline the key requirements and steps involved in the naturalization process, helping you understand the path to U.S. citizenship. We’ll cover eligibility criteria, application procedures, and the benefits of becoming a naturalized American.
What is Naturalization?
Definition and Process
Naturalization is the legal process that transforms a foreign national into a U.S. citizen. This process opens doors to new opportunities and rights in the United States. The Law Offices of Jeffrey A. Thompson has guided many clients through this transformative journey, providing expert assistance at every step.
Importance in U.S. Immigration
Naturalization holds a significant place in U.S. immigration policy. It allows immigrants to fully integrate into American society, granting them the right to vote, hold public office, and access federal jobs. The U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) reported that 818,500 immigrants became U.S. citizens through naturalization in fiscal year 2024. This number indicates a strong interest in U.S. citizenship.

Historical Context
The history of naturalization in the U.S. dates back to the country’s founding. The first naturalization law came into effect in 1790, establishing a two-year residency requirement. These laws have evolved over time to reflect changing societal values and immigration patterns. A notable change occurred with the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965, which eliminated national-origin quotas and significantly impacted the pool of potential U.S. citizens.
Current Requirements
Today’s naturalization process follows the guidelines set by the Immigration and Nationality Act. Key requirements include:
- Age requirement of 18 years or older
- Lawful permanent resident status for at least 5 years (or 3 years if married to a U.S. citizen)
- Proof of continuous residence and physical presence in the U.S.
- Demonstration of good moral character
- Successful completion of English language and civics tests
These requirements ensure that new citizens understand and commit to American values and principles.
The Path to Citizenship
The journey to U.S. citizenship through naturalization involves several steps. Applicants must navigate a complex process that includes filing forms, attending interviews, and passing tests. The next section will explore these steps in detail, providing a roadmap for those aspiring to become U.S. citizens.
Who Can Apply for Naturalization?
Age and Residency Requirements
To apply for naturalization, an individual must be at least 18 years old and a lawful permanent resident (LPR) of the United States. The general rule requires an applicant to have been an LPR for at least five years before applying. However, this requirement reduces to three years for those married to a U.S. citizen.
USCIS data from fiscal year 2024 shows that most people who naturalized were eligible based on being LPRs for at least 5 years. This statistic underscores the importance of maintaining LPR status before citizenship application.
Continuous Residence and Physical Presence
Continuous residence means an applicant has maintained their primary home in the U.S. for the required period (five years for most, three years for those married to U.S. citizens). Extended absences from the country can disrupt this continuity.
Physical presence refers to the actual time spent in the U.S. during the required period. An applicant must have been physically present in the country for at least half of the required residency period. For instance, a five-year continuous residence requirement necessitates at least 30 months of physical presence in the U.S.
Good Moral Character Demonstration
Good moral character stands as a key requirement for naturalization. USCIS evaluates an applicant’s conduct during the statutory period (typically the five years preceding the application) and beyond. This assessment includes a review of criminal records, tax payment history, and overall behavior as a law-abiding resident.
Applicants must disclose any criminal history, including minor offenses, in their application. Failure to do so can result in denial of the naturalization request. Those with concerns about their record should consult with an experienced immigration attorney.
Language and Civics Knowledge Requirements
English proficiency is fundamental for naturalization. Applicants must demonstrate the ability to read, write, speak, and understand basic English. This assessment occurs during the naturalization interview.
Additionally, applicants need to pass a civics test that evaluates their knowledge of U.S. history and government. The test consists of 100 questions, from which up to 10 are asked during the interview. A correct answer to at least 6 questions is required to pass.
Understanding these eligibility requirements marks the first step towards achieving U.S. citizenship. The next section will outline the steps involved in the naturalization process, providing a clear roadmap for those ready to embark on this significant journey.
How to Navigate the Naturalization Process
Submitting Your Application
The naturalization process begins with the submission of Form N-400, Application for Naturalization. This document requires detailed information about your background, residence history, and eligibility. In fiscal year 2024, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) received approximately 823,700 naturalization applications (a 5% increase from the previous year). Accurate and complete form submission prevents delays or denials.
Your application should include all necessary supporting documents (green card, passport, tax returns, and marriage certificate if applicable). The current filing fee for Form N-400 is $760 (as of April 2024). Fee waivers are available for eligible applicants earning under 400% of the federal poverty line.
Biometrics and Background Check
After USCIS receives your application, they schedule a biometrics appointment. This appointment involves taking your fingerprints, photograph, and signature for background check purposes. The process typically lasts about 20 minutes.
USCIS conducts thorough background checks using various government databases. This step verifies your eligibility and ensures you meet the good moral character requirement. Any discrepancies or undisclosed information can complicate your application process.
The Naturalization Interview and Test
The naturalization interview represents a pivotal moment in your citizenship journey. A USCIS officer reviews your application, asks questions about your background, and assesses your eligibility. They also evaluate your English language skills through casual conversation and by asking you to read and write simple sentences.
The civics test occurs during this interview. You’ll answer up to 10 questions from a list of 100 potential questions about U.S. history and government. To pass, you must correctly answer at least 6 out of 10 questions. In fiscal year 2024, the initial pass rate for the naturalization test was 89.7%, with a cumulative pass rate (including re-exams) of 94.4%.
Taking the Oath of Allegiance
If USCIS approves your application, the final step involves attending a naturalization ceremony where you take the Oath of Allegiance. This solemn promise includes pledging to support the Constitution and renouncing all allegiance to any foreign state or sovereignty. In fiscal year 2024, over 818,500 individuals took this oath, joining the ranks of naturalized U.S. citizens.
The naturalization process can take time (the average processing time currently stands at five months). However, proper preparation and guidance can help you navigate this journey successfully. The Law Offices of Jeffrey A. Thompson supports clients through each step, ensuring they’re well-equipped to achieve their goal of U.S. citizenship.

Final Thoughts
The rules of naturalization establish a comprehensive framework for immigrants to become U.S. citizens. These requirements include age and residency criteria, continuous presence, good moral character, and proficiency in English and civics. Professional legal assistance proves invaluable in navigating this complex process and avoiding potential pitfalls that could delay or derail an application.
Law Offices of Jeffrey A. Thompson specializes in guiding clients through every step of the naturalization journey. Our expertise in immigration law ensures that applicants are well-prepared for interviews, tests, and the overall process. The benefits of becoming a U.S. citizen through naturalization are numerous and life-changing (including the right to vote, hold public office, and access federal jobs).
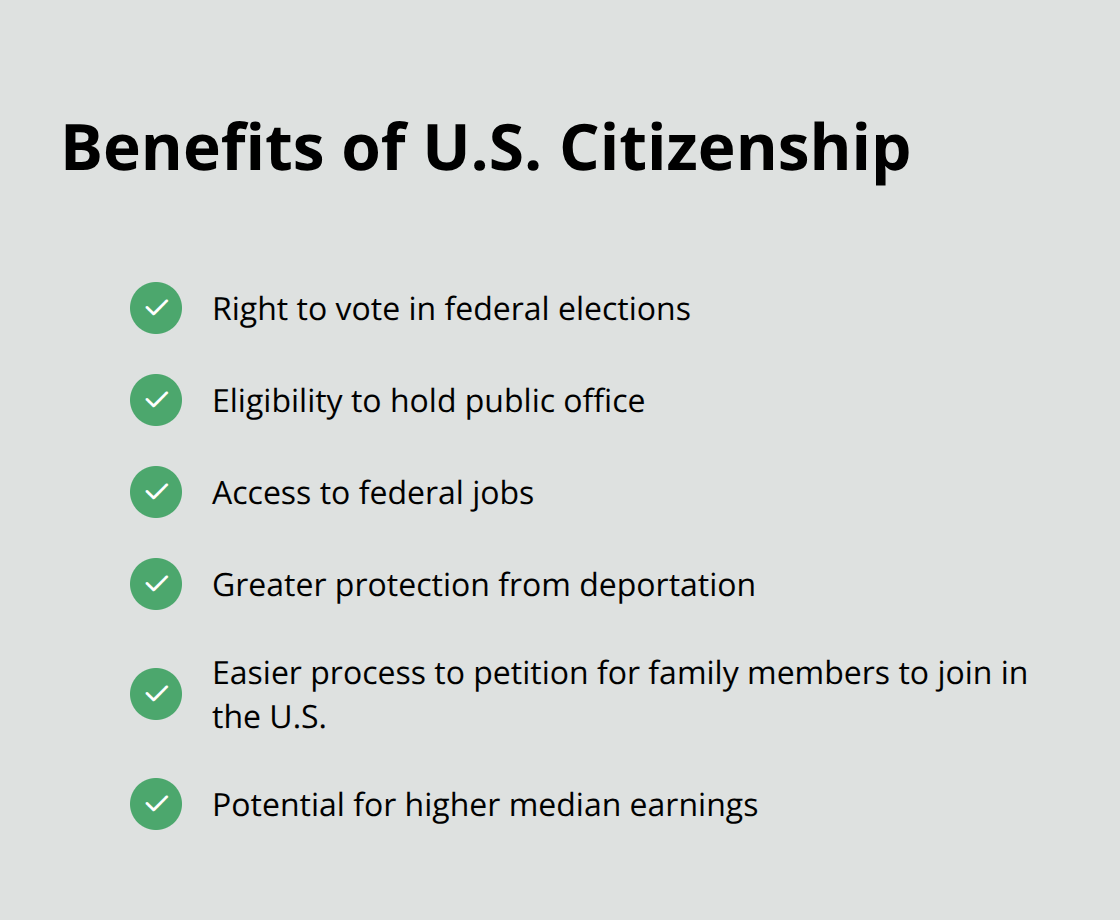
Naturalized citizens enjoy greater protection from deportation and can petition for family members to join them in the U.S. more easily. Data shows higher median earnings for naturalized citizens compared to non-citizens, often leading to improved economic outcomes. The journey to citizenship represents not just a legal change in status, but a profound personal commitment to the United States.


